DIGITAL HEALTH TOOLS
Our main digital tools are:

Digital health tools
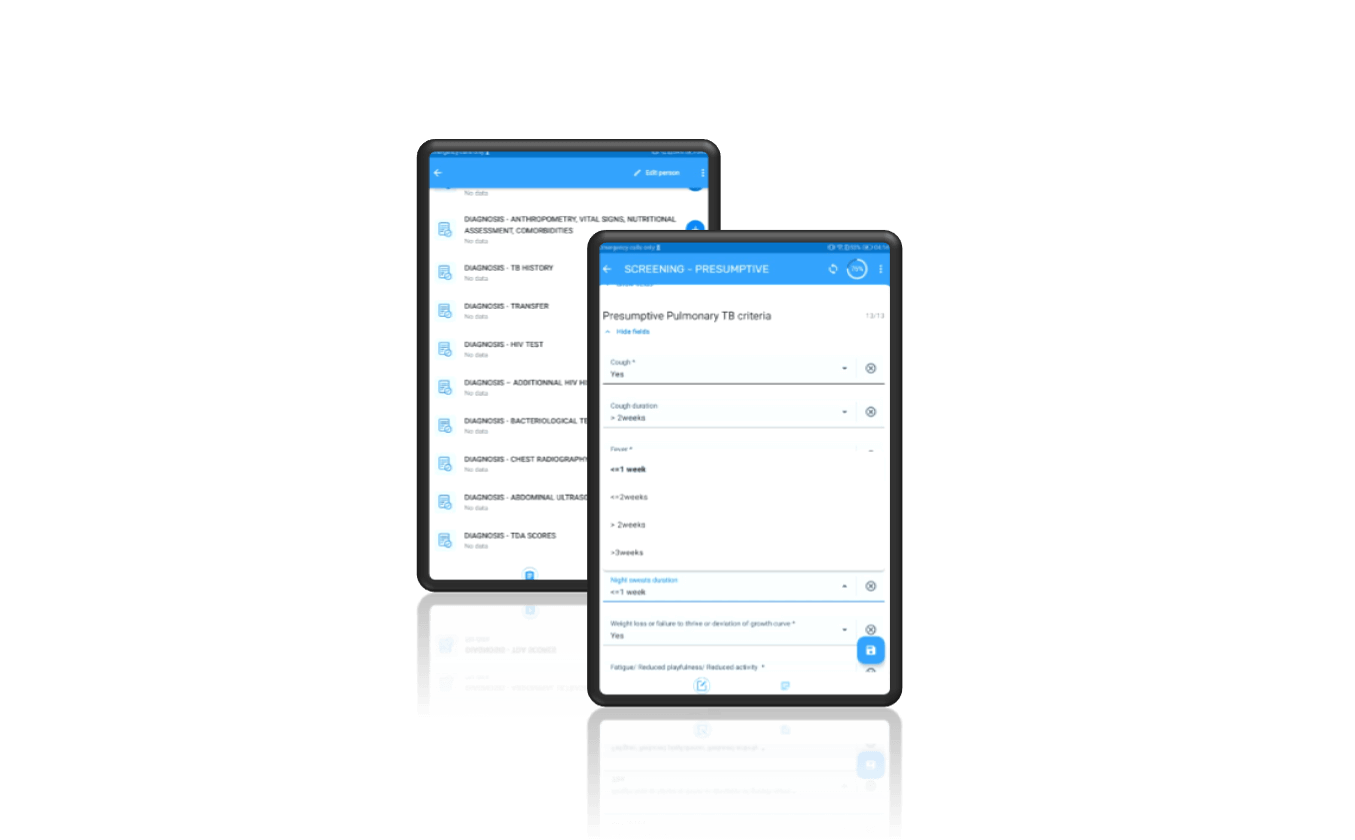
Transform complex Treatment Decision Algorithms (TDAs)
The eHealth4ChildTB project develops innovative digital tools to support health workers in diagnosing and treating childhood tuberculosis (TB). These tools transform complex Treatment Decision Algorithms (TDAs) into simple, user-friendly applications that can be used on tablets or smartphones in everyday clinics, including those with limited resources.
Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS):
Mobile or tablet applications that guide health workers step by step through the TDA process. Instead of memorizing complex scoring systems, a nurse or doctor simply enters a child’s symptoms, test results, or chest X-ray findings into the app. The CDSS then calculates the score automatically and suggests whether TB treatment should be started. This ensures decisions are more accurate and consistent, even for staff with limited TB experience.
Digital chest X-ray analysis with artificial intelligence (AI):
In many clinics, radiologists are not available, and chest X-rays can be difficult to interpret. AI technology can analyze digital X-ray images and highlight signs that may suggest TB. This helps health workers make better decisions, speeds up diagnosis, and reduces the risk of missed cases—especially important for young children whose symptoms are often unclear.
Lung ultrasound:
Unlike X-rays, ultrasound devices are portable, radiation-free, and relatively low-cost. eHealth4ChildTB is exploring how lung ultrasound can detect TB-related changes in children’s lungs and monitor their response to treatment. If effective, this tool could become a practical solution for rural or under-equipped clinics.
Integration with national health information systems:
Beyond helping with individual diagnoses, the project also links digital tools to existing reporting platforms used by national TB programs. This allows patient information to be securely recorded, making it easier to track progress, supervise care, and plan resources. It improves data quality, reduces paperwork, and supports better decision-making at district and national levels.
Together, these innovations aim to strengthen frontline care, reduce delays in treatment, and make advanced diagnostic support accessible to children and families in high-burden countries.
